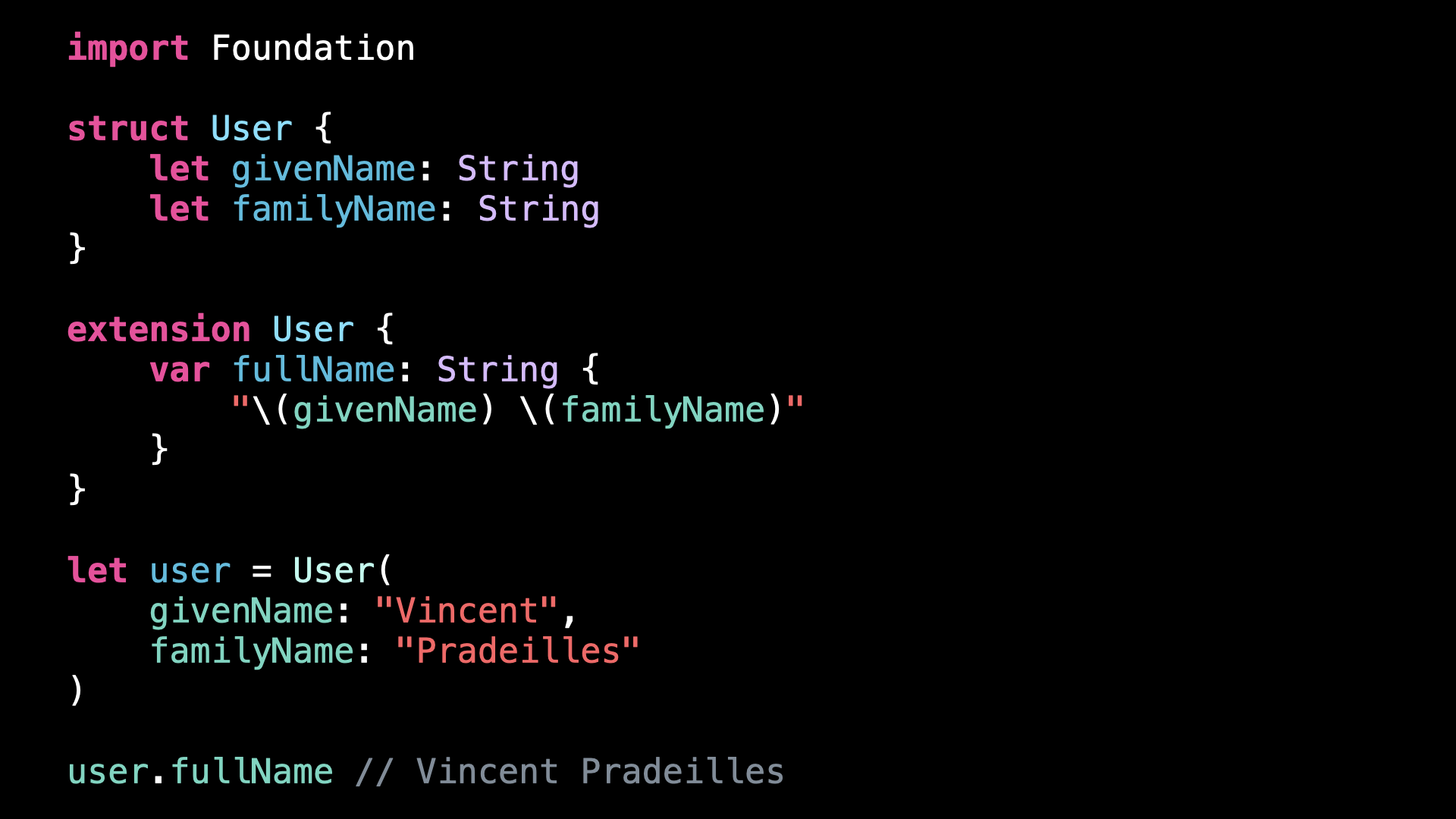
Bad practice: not using PersonNameComponentsFormatter
You’re more of a video kind of person? I’ve got you covered! Here’s a video with the same content than this article 🍿
Can you guess what’s the problem with this code?
If you live in a western country, there’s a good chance this code seems perfectly reasonable: we format the fullName of the User by using String interpolation.
However, while most western countries indeed format a fullName by writing the givenName first and the familyName second, not all countries follow this convention!
For instance, Koreans write the familyName first and the givenName second.
And as you can imagine, if your app doesn’t follow this local convention, it will feel weird and out-of-place with a part of your audience!
Fortunately, iOS has a built-in way to solve this problem!
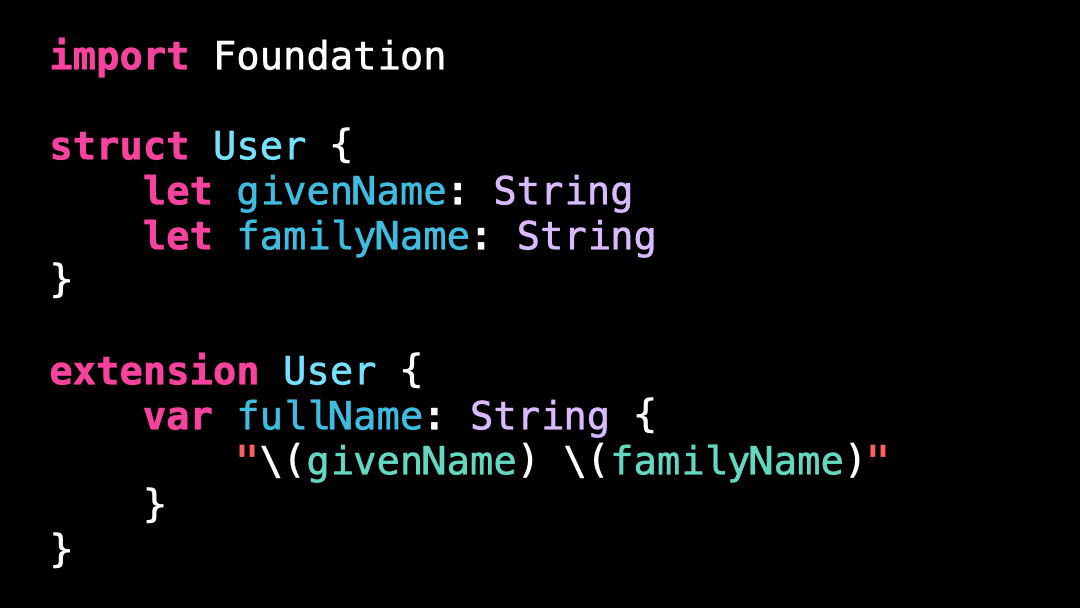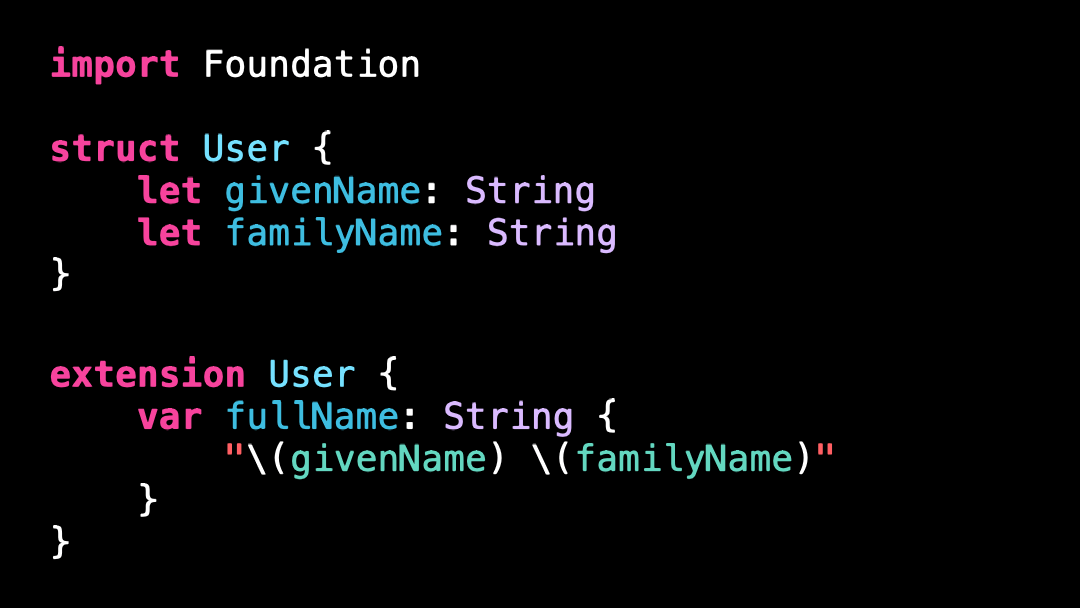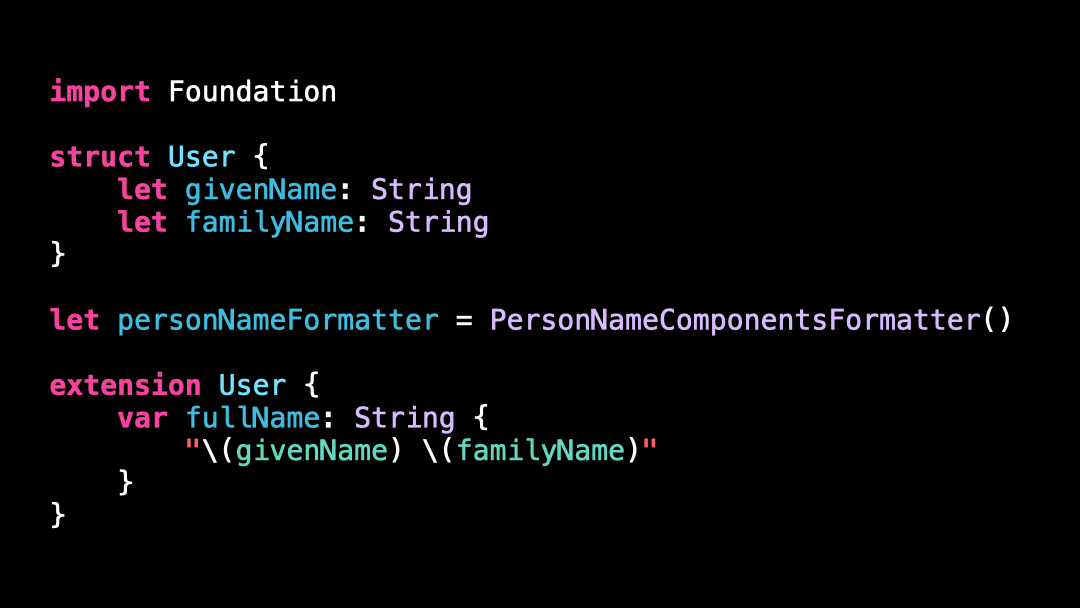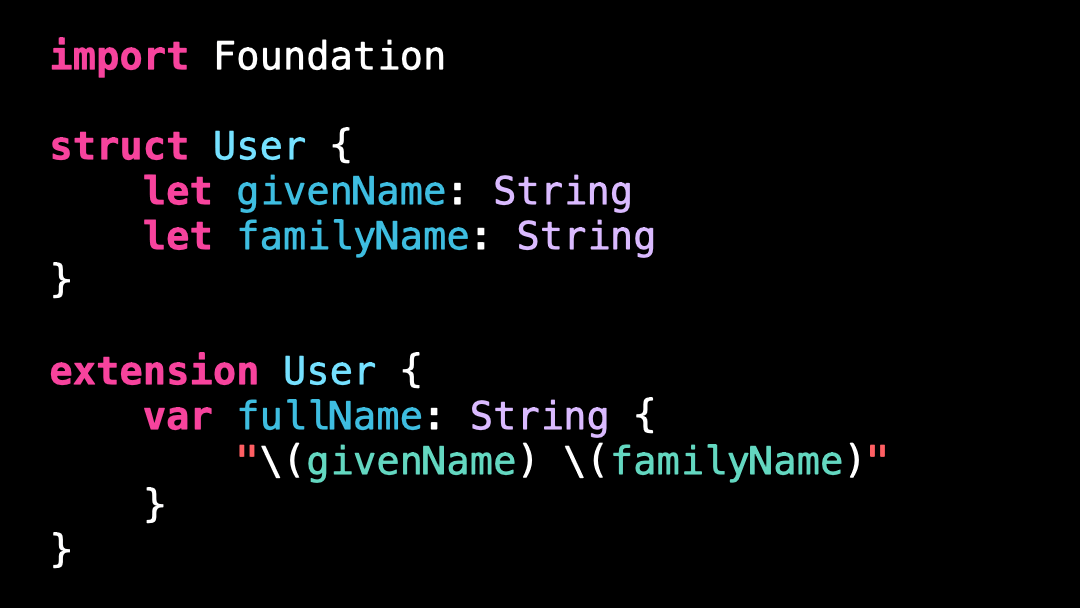
For this, we’re going to use a class called PersonNameComponentsFormatter.
PersonNameComponentsFormatter works in a similar way to other formatters like NumberFormatter or DateFormatter: you give it raw data and it formats it according to the user’s Locale.
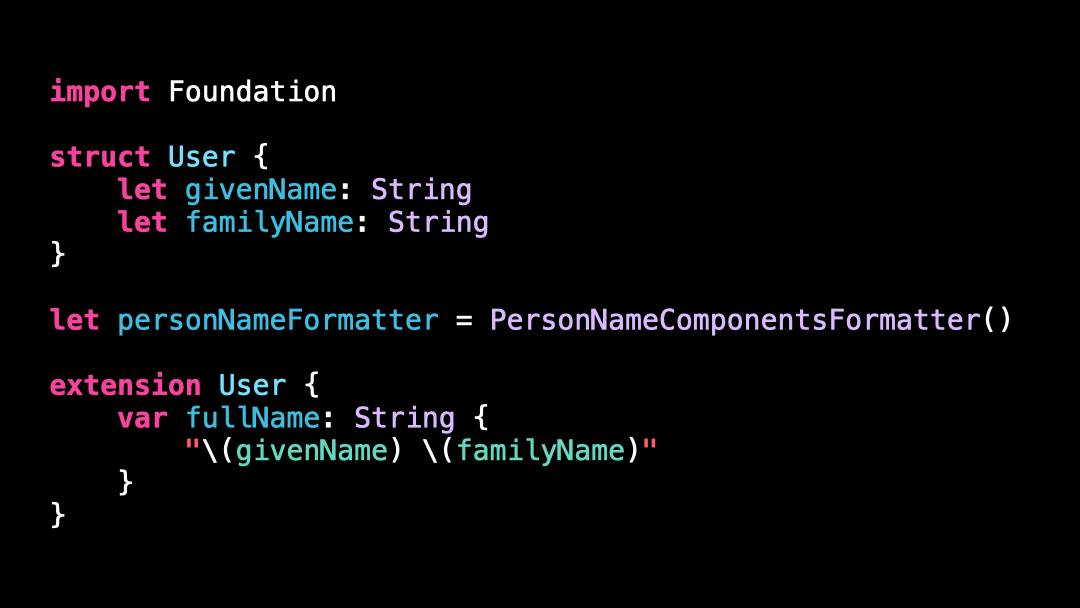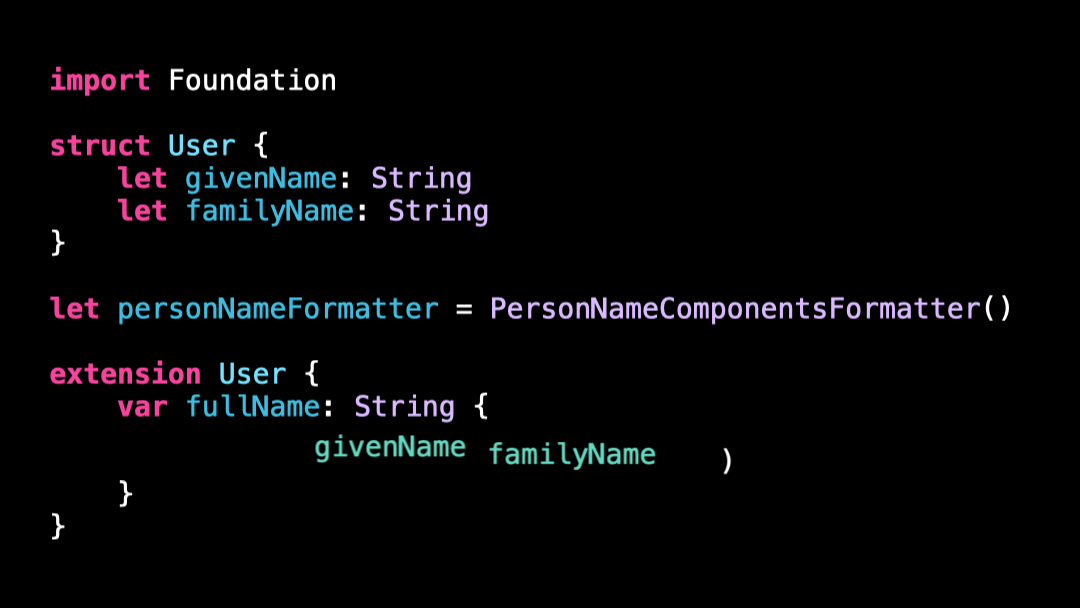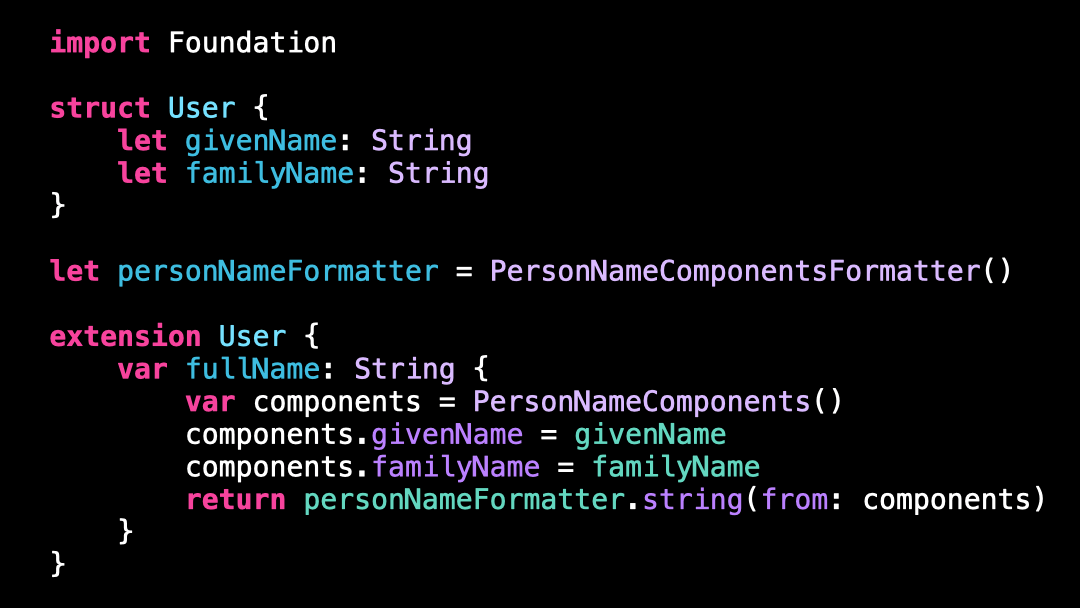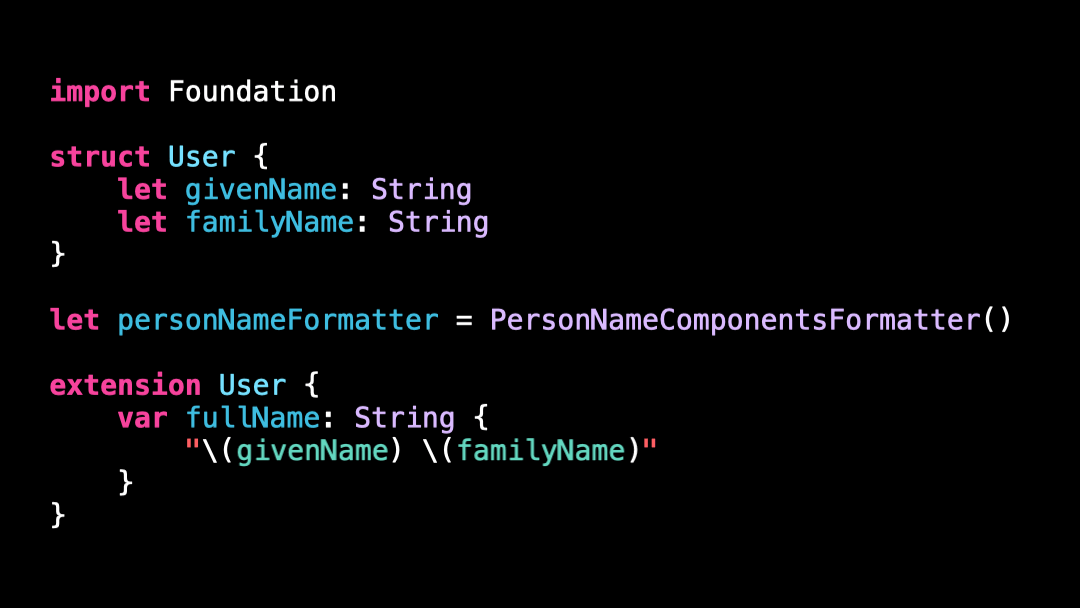
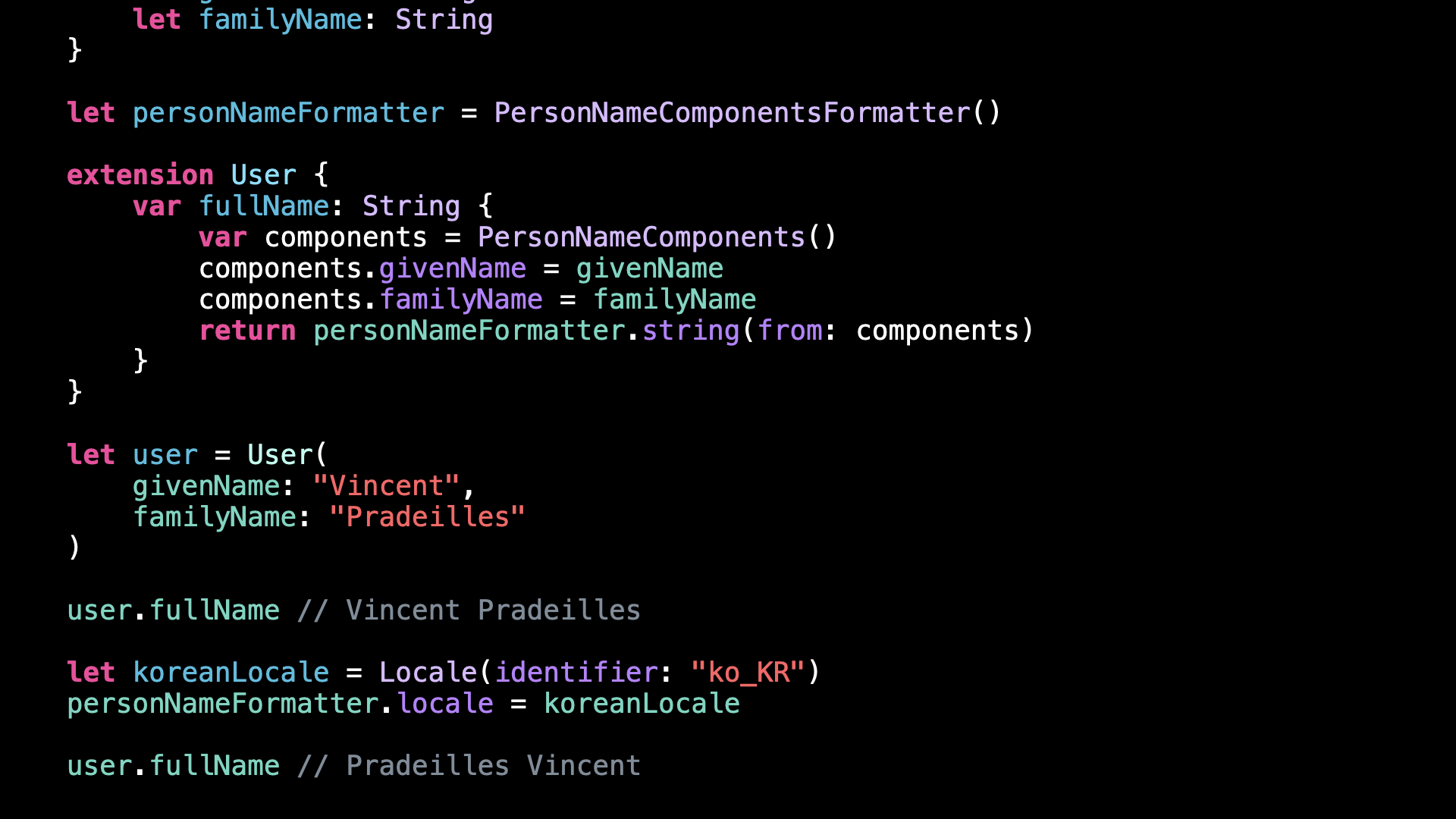
So I’m going to update the implementation of the property fullName to use a PersonNameComponentsFormatter rather than String interpolation.
As you can see, the new implementation yields the same result than the previous one:
That’s normal because my Locale is currently set to French, and this is indeed how a fullName would be displayed in France.
But if I update the Locale to be that of Korea, you can see that the behavior of the formatter is now matching that of the new Locale: the fullName is now formatted with the familyName first, and the givenName second.
That’s all for this article, I hope you’ve enjoyed discovering how PersonNameComponentsFormatter works!
Here’s the code if you want to experiment with it:
import Foundation
struct User {
let givenName: String
let familyName: String
}
let personNameFormatter = PersonNameComponentsFormatter()
extension User {
var fullName: String {
var components = PersonNameComponents()
components.givenName = givenName
components.familyName = familyName
return personNameFormatter.string(from: components)
}
}
let user = User(
givenName: "Vincent",
familyName: "Pradeilles"
)
user.fullName // Vincent Pradeilles
let koreanLocale = Locale(identifier: "ko_KR")
personNameFormatter.locale = koreanLocale
user.fullName // Pradeilles Vincent